

NaOH) (see hydrolysis of esters for more details) Amide preparation : heat with the amine, methyl or ethyl esters are the most reactive Hydrolysis of Esters Transesterification : heat with alcohol and acid catalyst Hydrolysis : heat with aq.

Introduction to Esters Reactions Esters can be converted into other esters (transesterification), the parent carboxylic acid (hydrolysis) or amides (see above). Concentrated sulfuric acid is often used. methanol + butanoic acid methyl butanoate + water A catalyst is needed to speed up the reaction. ethanol + ethanoic acid ethyl ethanoate + water Making an ester Higher tier You can make a variety of esters by reacting different carboxylic acids with different alcohols.
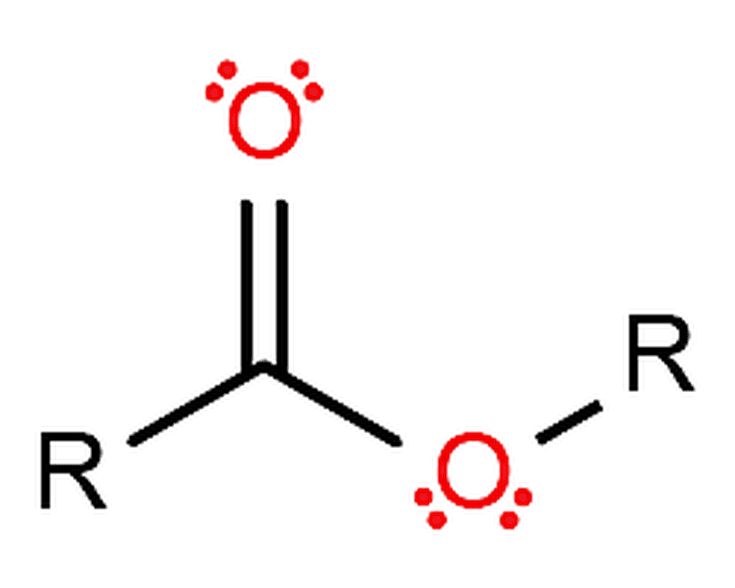
An example of this reaction is presented below: The products of this reaction are the alcohol and the salt of the carboxylic acid used to create the ester. Saponification This is the process by which an ester is hydrolyzed in the presence of a base. Dry hydrogen chloride gas is used in some cases, but these tend to involve aromatic esters (ones where the carboxylic acid contains a benzene ring). The catalyst is usually concentrated sulphuric acid. Esters are produced when carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. A mineral acid catalyst is usually needed to make the reaction occur at a useful rate. The most common method for preparing esters is to heat a carboxylic acid, R-CO-OH, with an alcohol, R'-OH, while removing the water that is formed. Esterification is the chemical process for making esters, which are compounds of the chemical structure R- COOR', where R and R' are either alkyl or aryl groups. This is the process you will be using today. This mixture is generally refluxed for a brief time to drive the reaction to completion. Fischer esterification involves mixing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol with a small amount of acid. Preparation of Esters The most common way to make simple esters is by Fischer Esterification, named after the German chemist Emil Fischer, who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1902. Condensed Structural Formula Name Melting Point (C) Boiling Point (C) Aroma HCOOCH3 methylformate 99 32 HCOOCH2CH3 ethylformate 80 54 rum CH3COOCH3 methylacetate 98 57 CH3COOCH2CH3 ethylacetate 84 77 CH3CH2CH2COOCH3 methylbutyrate 85 102 apple CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3 ethylbutyrate 101 121 pineapple CH3COO(CH2)4CH3 pentylacetate 71 148 pear CH3COOCH2C6H5 isopentylacetate 79 142 banana CH3CH2CH2COO(CH2)4CH3 benzylacetate 51 215 jasmine CH3CH2CH2COOCH4CH3 pentyl 73 185 apricot Properties of Esters *Polar -Lessthanalcohols,carboxylicacids -Solubleinwater *Smell Fruity *Can form Polymers Estersaremorepolarthanethers,butlesssothanalcohols.They participateinhydrogenbondsashydrogenbondacceptors,butcannotact ashydrogenbonddonors,unliketheirparentalcoholsandcarboxylic acids.Thisabilitytoparticipateinhydrogenbondingconferssomewater- solubility,dependingonthelengthofthealkylchainsattached.Sincethey havenohydrogensbondedtooxygens,asalcoholsandcarboxylicacidsdo, estersdonotself-associate.Consequently,estersaremorevolatilethan carboxylicacidsofsimilarmolecularweight. For example, ethanoic acid is more commonly known as acetic acid, and thus its esters contain "acetate" instead of "ethanoate"intheirnames.Othersuchsubstitutionsinclude "formate"insteadof"methanoate,""propionate"insteadof "propanoate," and "butyrate" instead of "butanoate." Inthecaseofestersformedfromcommoncarboxylic acids, more colloquial terms are sometimes used. Esternamesarederivedfrom theparentalcoholandacid. Nomenclature Theword"ester"was coinedin1848byGerman chemistLeopoldGmelin, probablyasacontractionofthe GermanEssigther,meaning aceticether. Theodorsofflowersandtheodorsandflavors offreshfruitsarearesultofacomplexmixture ofmanychemicalcompounds,butoneofthe majorconstituentsisatypeofcompoundcalled anester. Esternamesarederivedfromtheparentalcoholandthe parentacid.Whilesimpleestersareoftencalledby theircommonnames,allesterscanbenamedusingthe systematicIUPACname,basedonthenamefortheacid followedbythesuffix"-oate." KEY POINTS Estersareafunctionalgroupcommonlyencounteredin organicchemistry.Theyarecharacterizedbyacarbonbound tothreeotheratoms:asinglebondtoacarbon,adouble bondtoanoxygen,andasinglebondtoanoxygen.Thesingly boundoxygenisboundtoanothercarbon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
